What is taa marbuta? taa marbuta is the taa that always occurs at the end of certain nouns and adjectives. If connected to the preceding letter, it is written like this ـة, as in سَاعَة ‘watch’, فَاطِمَة ‘Fatima (name)’, and خَيْمَة ‘tent.’ If it occurs after one of the letters that do not connect to the following letter (i.e. ا, د, ذ, ر, ز,و) , it is written like this ة, as in زَهْرَة ‘flower’ زُبْدَة ‘butter’, فَتَاة ‘a girl.’ In writing, it is often confused with the haa ــه / ه, which is written without the two dots above it. In addition, since its pronunciation is the same as the pronunciation of the taa maftuha / mabsuta (i.e. ت) in connected speech; in genitive construction; and when vowelized, it is frequently confused with it in writing.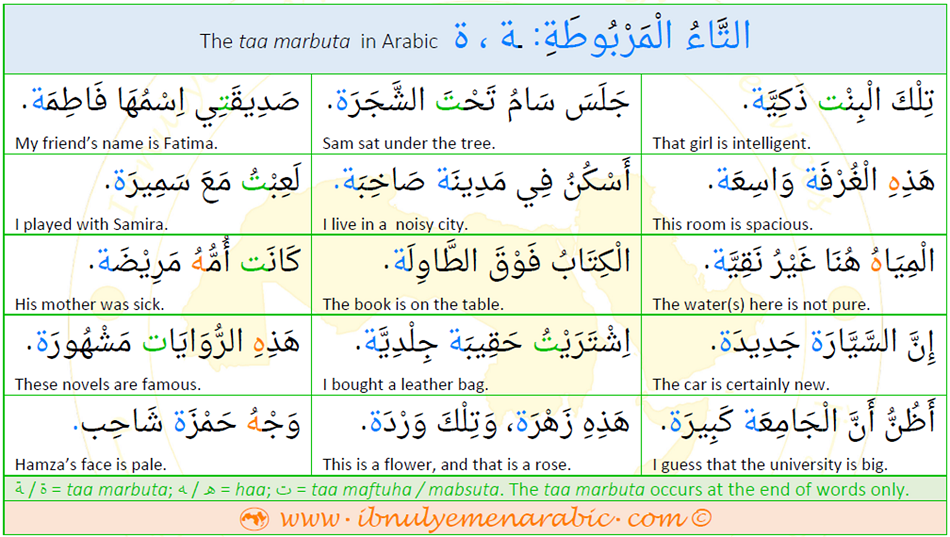
|
(A) The taa marbuta occurs at the end of feminine proper nouns, as in (1); at the end of some feminine singular noun that do not have corresponding masculine form, as in (2); at the end of some broken plurals, as in (3); and at the end of feminine singular adjectives that are derived from the corresponding masculine form (by adding the taa marbuta), as in (4). (B) The taa marbuta is written in two ways, that is ــة or ة, depending on the letter that precedes it. (C) The letter that precedes the taa marbuta always has a fatha - فَتْحَة over it as you can see in the list of examples. The only exception is the alif because it cannot be accompanied by any of the short vowels (i.e., fatha, dhamma, kasra). The alif is always saakin - سَاكِن, that is it has a sukuun over it. (D) The taa marbuta changes to regular taa (i.e. taa maftuha) ـتـ when pronominal suffixes (i.e., attached pronouns) are added to the nouns in which it occurs, as in (5). Compare the list to (2) above. |
(1) فَاطِمَة Fatima - عَائِشَة Aisha - خَدِيجَة Khadija (2) سَيَّارَة car - وَظِيفَة job - مِنْشَفَة towel (3) قُضَاة judges - حُمَاة protectors (4) جَمِيلَة beautiful - قَصِيرَة short - بَطِيْئَة slow (5) سَيَّارَتِي my car - وَظِيْفَتُكَ your job |
|
(A) The taa marbuta is added to the end of masculine adjectives and nouns to form the corresponding feminine form of these adjectives / nouns, as in (1). Therefore, the taa marbuta is the feminine marker in Arabic. |
(1) قَصِير ← قَصِيرَة short ، صَغِير ← صَغِيرَة small |
|
(B) The taa marbuta is added to the end of collective nouns to form a singular noun, as in (2). In such cases, the taa marbuta is a suffix for number (i.e., it means one) and for gender (i.e., a feminine marker). |
(2) عِنَب grapes ← عِنَبَة one grape |
|
(C) Certain nouns in Arabic do not have a masculine form. With these nouns, the taa marbuta is part of the word (i.e., not a suffix), as in (3). Still, it is a feminine marker. |
(3) بَقَرَة cow - شَجَرَة tree - سَلَّة basket |
|
(D) Sometime, the taa marbuta can indicate that the noun in which it occurs is a broken plural, that is the plural that does not follow the diacritical patterns of the singular, as in (4). |
(4) قَاضِي (قَاضٍ) judge ← قُضَاة judges |
|
(E) Many feminine proper nouns in Arabic end in taa marbuta, as in (5). |
(5) فَاطِمَة - سَعَادَة - شَرِيْفَة - فَوْزِيَّة - عَائِدَة - غَادَة - نُوْرَة - مُنِيْرَة - جَمِيْلَة - خَوْلَة - سَمِيْرَة - فَائِزَة - لَطِيفَة - وَرْدَة - عَبْلَة - صَفِيَّة - سُمَيَّة |
|
The taa marbuta ـة / ة is pronounced as haa ـه / ه when we pause on it, that is when there’s no short vowel (haraka - حَرَكَة: fatha, kasra, or dhamma) or tanween above it. A letter without haraka over it is called saakin - سَاكِن, that is it has a sukuun ( ْ ) above it. Therefore, when the taa marbuta is saakin(a), it is pronounced as haa. This does not affect the meaning, however.
Note: the الْ ‘the’ at the beginning of some of the words in the list is the definite article. |
سَارَة ← سَارَه سَمِيرَة ← سَمِيرَه نَادِيَة ← نَادِيَه .................................. الْوِسَادَة ← الْوِسَادَه مِسْطَرَة ← مِسْطَرَه الْخَرِيطَة ← الْخَرِيطَه غُزَاة ← غُزَاه .................................. فَرِيدَة ← فَرِيْدَه سَخِيفَة ← سَخِيفَه الضَّيِّقَة ← الضَّيِّقَه |
فَاطِمَة ← فَاطِمَه عَائِشَة ← عَائِشَه خَدِيجَة ← خَدِيجَه .................................. سَيَّارَة ← سَيَّارَه الْوَظِيفَة ← الْوَظِيفَه مِنْشَفَة ← مِنْشَفَه الْقُضَاة ← الْقُضَاه .................................. جَمِيلَة ← جَمِيلَه الْقَصِيرَة ← الْقَصِيرَه بَطِيئَة ← بَطِيئَه |
|
On the other hand, the haa ـه / ه is always pronounced as haa regardless of whether it has a haraka over it or not. |
مِيَاهٍ ← مِيَاه waters فِقْهًا ← فِقْه jurisprudence عَنْهُ ← عَنْه about him |
وَجْهٌ ← وَجْه face كِتَابِهِ ← كِتَابِه his book سَفِيْهًا ← سَفِيْه fool/foolish |
|
(1) سَيَّارَة مُحَمَّد Mohammed’s car - وَظِيْفَة سَارَة Sarah’s job خَرِيْطَة الْيَمَن Yemen's map - طَاوِلَة عَلِي Ali's table نَافِذَة سَلِيم Salim's window - سَاحَة الْبَيْت the house yard خَيْمَة الرَّجُل the man's tent - غُرْفَة النَّوْم the bedroom سَاعَة أخِي my brother's watch - كُوْفِيَّة سَام Sam's hat زَوْجَة الرَّجُل the man's wife - خَالَة أُمِّي my mum's aunt |
(A) These two-word phrases are called genitive construction (إِضَافَة - idafa). Both words must be nouns. The first noun is indefinite (نَكِرَة – nakira), and the second nous is definite (مَعْرِفَة – ma‘rifa). In such phrases, the taa marbuta must be pronounced as ت taa maftuha (not haa), regardless of whether it is vowelized or not. Therefore, it is incorrect to pronounce the taa marbuta in these phrases as haa. If this happens, meaning is significantly affected. |
|
(2) سَيَّارَةٌ ، السَّيَّارَةُ - خَرِيطَةٍ ، الْخَرِيطَةِ - سَاعَةً ، السَّاعَةَ |
(B) If the taa marbuta is vowelized (i.e. it has a short vowel or tanween marks over it), it must be pronounced like the taa maftuha ت, not haa. |
|
(3) السَّيَّارَةُ الْجَدِيدَةُ the new car كَتَبَتِ الطَّالِبَةُ الْوَاجِبَ the student (f) wrote the HW أَكْلَ الْوَلَدُ التُّفَّاحَةَ الْحَمْرَاءَ. the boy ate the red apple (4) السَّيَّارَةُ الْجَدِيْدَةُ ⇐ السَّيَّارَتُلْجَدِيْدَةُ كَتَبَتِ الطَّالِبَةُ الْوَاجِبَ ⇐ كَتَبَتِطَّالِبَتُلْوَاجِبَ أَكلَ الْوَلَدُ التُّفَّاحَةَ الحَمْرَاءَ ⇐ أَكَلَلْوَلَدُتُّفَّاحَتَلْحَمْرَاء |
(C) In connected speech, the taa marbuta must be vowelized to be pronounced as taa maftuha ت. In fact, it is the short vowel over it that makes connected speech possible, as in (3). In (4), spoken words are connected, alif, and alif and laam (with sun letters) are assimilated. Therefore, the whole phrase / sentence seem like one word (when spoken). If short vowels are not added over it, it is pronounced as haa. Speech, as a result, becomes broken and unnatural. That is, there will be a slight pause after each word when saying a sentence that expresses meaning. |
|
(5) دَرَسَتْ she studies - أَكَلْتُ I ate مَاتَ he died - بَيْت house وَقْت time - سُكُوْت silence سَافَرَتْ إِلَى الْيَمَن she travelled to Yemen |
(D) On the other hand, the taa maftuha is always pronounced as taa ت regardless of whether it has short vowels or tanween marks over it. Also, both in isolated words and in connected speech, it is always pronounced as taa ت. A pause on it does not affect its pronunciation. |